Introduction
The TIM API is the standard application interface for ECR integration using Worldline terminals.
TIM API provides a comprehensive feature set to support the requirements of several different markets. This guideline is intended to be used by ECR integrators that need to implement the TIM API functionality in their products.
The following document contains an overview structure, description of the TIM API modes synchronous/asynchronous and describes the corresponding functions, notifiers and data elements that can be used with the TIM API. Furthermore implementation examples are provided. Nevertheless always the corresponding description of a function or data element is authoritative, not the examples.
Setup Configuration
The configuration of the terminal can be done by creating and configuring a
terminal_settings-instance. The
terminal_settings-instance must then be passed to the
terminal_createfunction.
Once a
terminal-instance has been created with a
terminal_settings-instance, the settings can not be changed anymore.
Changes to the
terminal_settings-instance will be ignored.
The network and guides configuration are explained in the following
chapters.
For further information refer toterminal_settings.
Network Configuration
Depending on the platform used, the TIM API module can communicate with the Terminal over different communication channels.
The default communication is over TCP/IP connection. Default port used is 7784.
For TCP/IP connection there are two possible ways to connect to the terminal:
-
Broadcast-Mode:
- Terminal ID (TID) is known.
- The TIM API starts broadcasting on the default interface and connects to the connection information sent by the matching terminal.
-
Direct Connect:
- IP address of the terminal is known.
- Connection is established directly via IP.
Guides Configuration
There are various
guides
covering different use case scenarios. The guide retailis the basic guide and is activated as
default. With set_guides
the guides can be configured. Important: the configuration needs to include all desired guides
(including
the retail guide).
Code-example for creating a terminal including settings with activated guides retail and hospitality:
ta_object_t terminal = ta_object_invalid;
ta_object_t settings = ta_object_invalid;
// create terminal settings instance
ta_terminal_settings_create(&settings);
// add wanted guides (with bitwise or)
ta_terminal_settings_set_guides(settings, ta_c_guide_retail | ta_c_guide_dialog);
// create terminal
ta_terminal_create(&terminal, settings);
// release terminal settings
ta_object_release(settings);
//...
// in the end release terminal as well
ta_oject_release(terminal);Operation Overview
Follow these basic steps for using the TIM API:
- Create
terminal_settingsand initialize connection parameters (see Setup Configuration) - Create
terminalinstance using the createdterminal_settings - Set some properties where required:
- Define a
pos id -
create mandatory
list of
ecr_infoand add withta_terminal_add_ecr_data -
create list of
print_optionsand set withset_print_options ta_terminal_add_listeners
- Define a
-
connectandlogin. This can be done automatically, when the first terminal operation is called or manually using the login method. - Use terminal operation functions.
A basic flow to show a dialog is:
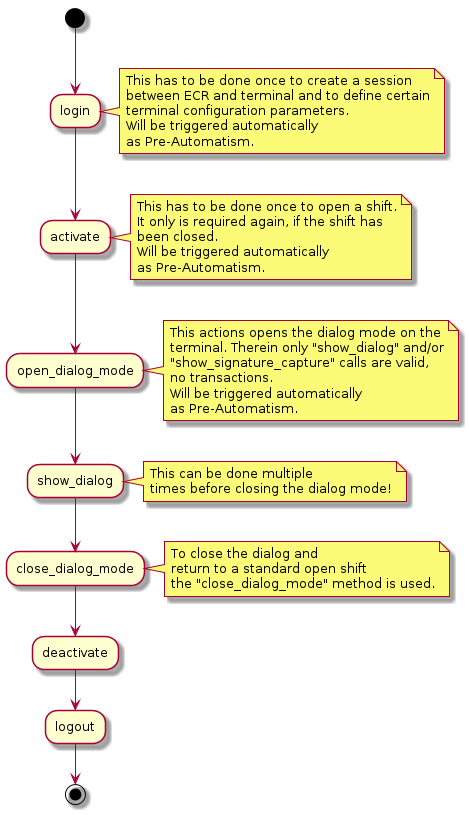
Automatisms
The TIM API uses two different types of automatisms:
-
Pre-Automatisms: This means that all actions that need to be done before a function can be called. E.g. a transaction can be called in disconnected state without having called connect, login and activate in advance. These are called automatically by the TIM API before the transaction is performed. The Pre-Automatisms are enabled by default.
-
Post-Automatisms: These automatisms can be enabled or disabled using the members
auto_commitandfetch_brands. A Post-Automatism is triggered after an action has been performed. E.g. if a connect has been called andfetch_brandsis activated, anapplication_informationrequest is called automatically after the connect. Or ifauto_commitis activated acommitis performed automatically after a transaction has been made.auto_commitandfetch_brandsare enabled by default.
The following diagramsshow the principle of the Pre-Automatisms and Post-Automatisms. Pre-Automatisms are enabled by default and cannot be disabled. If an error occurs the started request from the ECR is returned with an error.
Synchronous flow
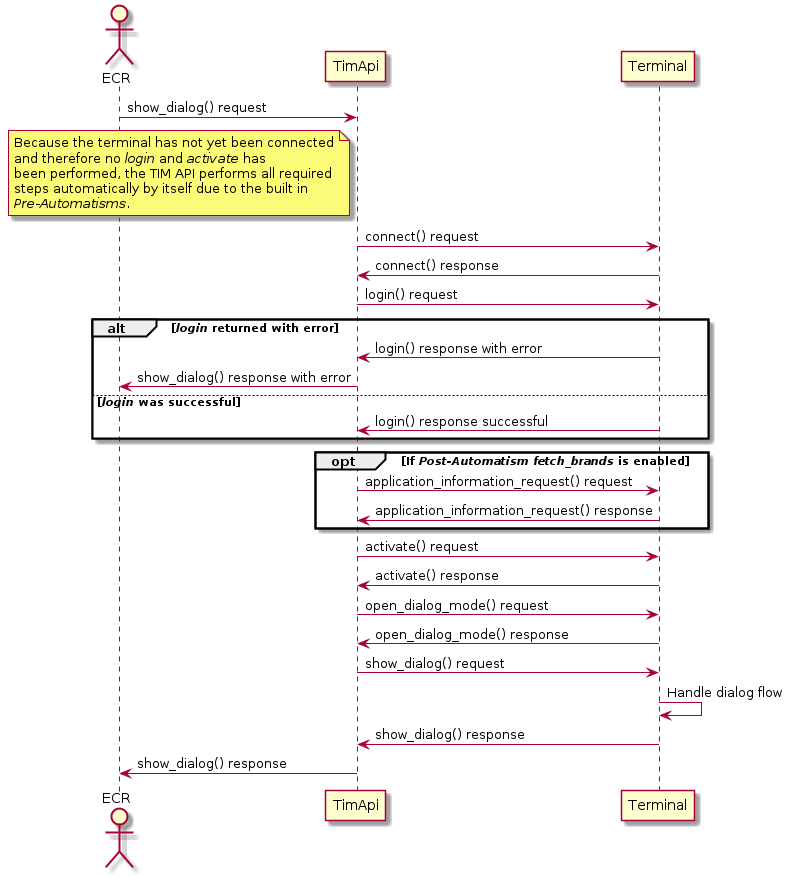
Asynchronous flow
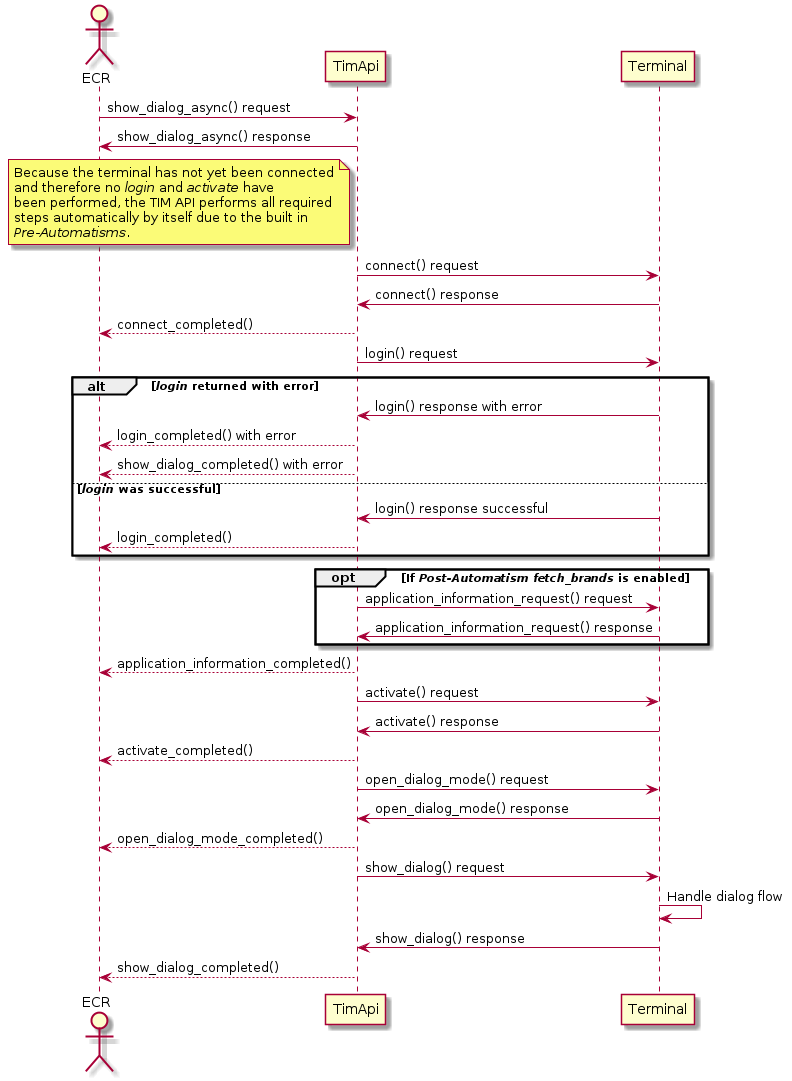
Use Cases
This chapter describes various guides and their use cases.
Hint: if no content visible, try to select a guide under "Guide Selection" on the left.
Manual Pan Key Entry
The TIM API offers the possibility to perform a Manual Pan Key Entry (MPKE) on ECR side, e.g. if no physical card is present.
This can be done by setting the card_ref field in the transaction_datacontainer
present in the terminal instance.
This card_ref field must have the following format to reference a non-PCI PAN:
Example: "061234567801234567" : "06" is the prefix that defines the content type that follows (non-PCI PAN), "1234568701234567" is then the non-PCI PAN.
Important: The MPKE on the ECR is only allowed for non-PCI brands, otherwise the manual entry must only be performed on the PIN Pad.
Guide Petrol Use Cases
Petrol functionality adds a number of
additional methods and notifiers,
transaction types,
containers (additional_info_list,
basket)
, container content (processing_disposition)
and flows
tailored to the needs at petrol stations.
Petrol has the following basic use cases:
Petrol Basket Handling
An essential part of the petrol use cases is the usage of the basket container.
This container is used to exchange information regarding purchased goods and fuel at a petrol station. It is important to know that the correctness of the content
of the basket container lies within the responsibility of the ECR and/or the acquiring host, not of the TIM API or the terminal.
The basket is sent from the ECR to the terminal, then from the terminal to the host.
The host may adjust the content of the basket depending on the card used for the transaction,
therefore the basket sent from ECR to terminal may differ from the
basket returned from terminal to ECR.
A basket may be used with the following transaction_types:
- Purchase
- FinalizePurchase
To send a basket within a request, the transaction_request
must be created by the integrator and the basket
and its basket_items must then be set in the transaction_request.
The transaction_request is then used as parameter of the transaction/
transaction_async
function.
Indoor - Online Card
Online cards are processed like a standard credit or debit payment card through an online system,
no mather if it is a standard credit card or an oil company card. In the latter case however,
depending on the exact brand rules, additional data must be supplied by the ECR system
(usually the type of goods being purchased, see basket)
and may be collected form the cardholder (e.g. ID number) and sent on to the online system.
The data is also provided back to the ECR via the basket
and additional_info_list containers.
An online system may decline parts of the purchase basket.
The transaction flow differs from the standard scenario in an additional way. To distinguish
between online cards (this scenario) and offline cards
(that scenario ) it is
necessary to first initiate a card detection through an
ta_terminal_init_transaction call.
This is an indoor scenario, i.e. takes place in an attended environment, usually a shop that is part of the petrol station. See this flow for reference.
Outdoor - Online Card
Outdoor - Online Card is esentially the same scenario as above. The difference is that it takes place on an unattended terminal generally located at or near the petrol pump.
This scenario requires that exchange of goods for money is slightly altered. The new
sequence of events is: check if sufficient funds are available, hand out goods, finalize
the funds transfer after the final amount is known. This is supported through the
transaction types pre_authorization and
finalize_purchase.
This is an outdoor scenario, i.e. takes place in an unattended environment, usually at the petrol pump. See this flow for reference.
Indoor - Offline Card
Offline cards are cards that are processed entirely by the ECR system. The EFT operates only
as a card reader, display and keyboard for the ECR. The ECR recognises offline cards based on
the processing_disposition
returned from ta_terminal_init_transaction.
After the completion of ta_terminal_init_transaction
the ECR is responsible for all further interaction. For cardholder interaction a number of
dialogs (part of the "Dialog" guide) can be used.
This is an indoor scenario, i.e. takes place in an attended environment, usually a shop that is part of the petrol station. See this flow for reference.
Outdoor - Offline Card
Outdoor offline processing of cards does not differ from indoor online processing.
This is an outdoor scenario, i.e. takes place in an unattended environment usually at the petrol pump. See this flow for reference.
Guide Unattended Use Cases
Unattended functionality is aimed at the needs of vending machines an similar devices. It adds
additional methods,
transaction types and
flows.
Unattended has the following basic use cases:
Use Case Partial Commit
commit-function has an amount parameter.
See this flow for reference.
Use Case Hold Commit
Use Case Amount Adjustment
Use Case Retain Card
Use Case Silent Abort
Guide Banking Use Cases
Banking functionality adds an
additional methods and notifiers,
banking transaction types,
and
flows
tailored to the needs of banking use cases.
Banking guide offers the following use cases:
Balance Inquiry
To have an overview about the balance of the account, TIM offers a function
to check the current account balance of the card used. This function is called
ta_terminal_balance_inquiry and requires
a present card. To be sure that only the right cardholder is able to check his/her
account balance a PIN check will be performed.
See this flow for reference.
Client Identification
For certain banking actions it is required to identify the cardholder by performing
a PIN check. TIM offers this functionality using the "Dialog Mode" which requires the
"Dialog" guide as well, besides the "Banking" guide. The corresponding value for
resource_id used to show a PIN check dialog is
pin_check.
See this flow for reference.
Signature Capture
Besides checking the PIN of a customer it may be required that a customer has to sign
to perform a certain action. TIM offers a signature capture functionality. This function
requires the "Dialog" guide to be active, besides the "Banking" guide, if used in banking environment.
The corresponding function ta_terminal_show_signature_capture
is shown more detailed in the "Dialog" guide.
See this flow for reference.
Card Identification
As there might be some special cards used in the banking environment and therefore special functions used,
TIM allows to make a card identification which delivers card_data to
determine which action should be done next, depending on the card data returned.
This function requires the "Dialog" guide to be active, besides the "Banking" guide. The corresponding values for
resource_id used to identify the card used, are either
swiss _post _card_identification for Swiss Post or
banking _card_identification for other Banking purposes.
See this flow for reference.
Account Transfer: Swiss Post only
A common use case at a bank is to transfer money from one account to another. To be able to use this feature
the "Dialog" guide is required besides the "Banking" guide. TIM offers a function that allows to set the source account, the destination account
and the amount to transfer. The function ta_terminal_show_dialog_async with the
corresponding resource_id and the placeholder_items
must be used. The correct resource_id is
inter_account_transfer and the following
placeholder_items are required to be set in the
show_dialog_request:
- 0: Source Account
- 1: Source Account Type
- 2: Currency Source Account
- 3: Source Account - Description
- 4: Destination Account
- 5: Destination Account Type
- 6: Currency Destination Account
- 7: Destination Account - Description
- 8: Currency
- 9: Amount
See this flow for reference.
Account Deposit: Swiss Post only
Another use case is that the customer wants to deposit an amount on his/her account. To be able to use this feature
the transaction_type "AuthorizeDeposit" is introduced in the "Banking" guide. This is done with the function
ta_terminal_transaction_async and the
corresponding transaction_type.
See this flow for reference.
Account Payout: Swiss Post only
A similar use case as above is that the customer wants to withdraw an amount from his/her account. To be able to use this feature
the "Dialog" guide is required besides the "Banking" guide. This is also done with the function
ta_terminal_show_dialog_async and the
corresponding resource_id and placeholder_items.
The correct resource_id is
disbursement_from_account and the following
placeholder_items are required to be set in the
show_dialog_request:
- 0: Debit Account
- 1: Debit Currency
- 2: Amount
See this flow for reference.
Parcel Acknowledgement: Swiss Post only
This next use case is that a customer wants to pick up a parcel and must sign on the device to acknowledge that he/she actually picked up the parcel.
As this requires the signature input of the customer it is offered as dialog function
ta_terminal_show_dialog_async and the
corresponding resource_id. This requires an activeted "Dialog" guide.
The correct resource_id is
packet_acknowledgement, There are no
placeholder_items required.
See this flow for reference.
Load PrePaid Phone: Swiss Post only
Another use case is to load a pre paid phone. This is also done with the function
ta_terminal_show_dialog_async and the
corresponding resource_id and placeholder_items.
The correct resource_id is
show_phone_number_with_amount and the following
placeholder_items are required to be set in the
show_dialog_request:
- 0: Phone number
- 1: Currency
- 2: Amount to load
See this flow for reference.
Guide Austrian Use Cases
The Austria guide adds two new use cases:
- Non guaranteed payment (NGV)
- Delayed payment
Both use cases do not add any new functions.
Only the standard ta_terminal_transaction_async
and ta_terminal_transaction functions with
transaction_type _purchase are
used with additional parameters the can be set in transaction_data
before starting the purchase transaction.
Austrian Use Case: NGV
An NGV payment is used in conjunction with a standard purchase transaction. The difference is that the purchase is handled
as an own risk transaction for the merchant.
Before starting a purchase transaction the ngv_mode can be set
according to ngv_mode to define the NGV behaviour of a transaction.
With the ngv_mode it is possible to either forbid NGV usage for the next transaction,
to allow it with a fallback to a standard purchase transaction or to set NGV usage to mandatory.
- If the NGV usage is explicitly forbidden the purchase transaction must be performed as a standard purchase.
- If the NGV is wished but fallback is allowed it is possible that the current purchase will either be performed as an NGV purchase or automatically as a standard purchase in case it is not possible to make an NGV purchase.
- If NGV usage is set to mandatory the current purchase transaction must be performed as an NGV purchase. If this is not possible the purchase transaction fails without fallback.
To identify if the current transaction has been performed as an NGV purchase or not a new boolean flag ngv_used_flag
has been introduced in the transaction_response. For statistics the NGV transactions can also be identified
in the counters using the same ngv_used_flag.
Austrian Use Case: Delayed Payment
The delayed payment can only be used in conjunction with an NGV purchase.
For delayed payments, the clearing of a transaction is delayed by the clearing house for the defined number of days.
The delay is set using the clearing_delay member in
transaction_data.
Terminal methods overview
The basic operation modes of terminal function calls are:
-
Synchronous
Function calls are blocking and return after the operation has finished. Error code is provided and indicates if request was successful or not. -
Asynchronous
Function call returns immediately after the operation has started successfully. A user-implemented callback function will then be called, after the operation has finished. All callback functions receive anevent. Theeventcontains aresult_codeindicating if there were errors or not. The user-implemented callback function has to be registered withadd_listener.
Functions called on terminal perform synchronous by default. The asynchronous method has the same name with _aync appended to its name.
Code example for adding a terminal listener:
/*
* Example for adding a terminal status listener
*
* \param[in] terminal Terminal instance
*/
void add_status_listener(ta_object_t terminal) {
ta_object_t listener = ta_object_invalid;
ta_s_terminal_listener_t listener_config;
// clear listener-config
memset(&listener_config, 0, sizeof(listener_config));
// add user-implemented callback to listener-config
listener_config.terminal_status_changed = mylistener_terminal_status_changed;
// optional: add user content to listener,
// pointer will be handed over to all callbacks:
//listener_config.user_pointer = &custom_struct;
// create listener-object
ta_terminal_listener_create(&listener, &listener_config);
// add listener-object to terminal
ta_terminal_add_listener(terminal, listener);
// release listener-object
ta_object_release(listener);
}
/*
* Callback for terminal status changes
*
* Will be called when status of terminal changes.
* \param[in] terminal Terminal instance
* \param[in] user_pointe User-pointer which can be set in the terminal listener
*/
void mylistener_terminal_status_changed(ta_object_t terminal, void *user_pointer) {
// implement your code to process status change here...
//printf(" > listener_terminal_status_changed\n");
}Main / guide Retail terminal functions
Guide Petrol terminal functions
|
Sync method
Async method Completed event |
Description |
|---|---|
ta_terminal_init_transaction
ta_terminal_init_transaction_async
init_transaction_completed
|
Retrieve card data for the presented card. |
Guide Unattended terminal functions
|
Sync method
Async method Completed event |
Description |
|---|---|
ta_terminal_open_reader
ta_terminal_open_reader_async
open_reader_completed
|
Opens the shutter of the card reader. |
ta_terminal_amt_adjustment
|
Send an amount adjustment notification to the terminal during an open transaction. The amount is used as the new amount for the transaction. |
ta_terminal_close_maintenance_window
ta_terminal_close_maintenance_window_async
close_maintenance_window_completed
|
Prohibits the EFT terminal from performing any triggered maintenance tasks. |
ta_terminal_close_reader
ta_terminal_close_reader_async
close_reader_completed
|
Closes the shutter of the card reader. |
ta_terminal_commit
ta_terminal_commit_async
commit_completed
|
Commits a transaction after succesful authorization. A lower amount may be commited than the authorized amount. |
ta_terminal_eject_card
ta_terminal_eject_card_async
eject_card_completed
|
Ejects the card from the card reader. |
ta_terminal_hold_commit
|
Increases the commit timeout. |
ta_terminal_open_maintenance_window
ta_terminal_open_maintenance_window_async
open_maintenance_window_completed
|
Opens a maintenance window where the terminal can perform all maintenance processes it was not able to perform before.> |
Banking terminal functions
|
Sync method
Async method Completed event |
Description |
|---|---|
ta_terminal_balance_inquiry
ta_terminal_balance_inquiry_async
balance_inquiry_completed
|
Perform a balance check of a card/account on the terminal. |
Guide Dialog terminal functions
|
Sync method
Async method Completed event |
Description |
|---|---|
ta_terminal_open_dialog_mode
ta_terminal_open_dialog_mode_async
open_dialog_mode_completed
|
Open dialog mode on the terminal. |
ta_terminal_close_dialog_mode
ta_terminal_close_dialog_mode_async
close_dialog_mode_completed
|
Close dialog mode on the terminal. |
ta_terminal_show_dialog
ta_terminal_show_dialog_async
show_dialog_completed
|
Show dialog on the terminal. |
ta_terminal_show_signature_capture
ta_terminal_show_signature_capture_async
show_signature_capture_completed
|
Show signature capture on the terminal. |
Additional terminal listener-events
| Listener-event | Description |
|---|---|
request_completed
|
Operation started by an asynchronous function has finished.
Applications can use both operation specific completion callback in combination with this generic completion callback. |
terminal_status_changed
|
The terminal status has changed. The new status can be
retrieved from the TerminalStatus property. |
Flows
This chapter describes various flows for specific guides.
Hint: if no content visible, try to select a guide under "Guide Selection" on the left.
Petrol Additional Flows
Petrol Flow: Indoor - Online Card
Petrol Flow: Outdoor - Online Card
Petrol Flow: Indoor - Offline Card
Petrol Flow: Outdoor - Offline Card
Guide Unattended Additional Flows
Flow: Partial Commit
Flow: Hold commit
Flow: Amount adjustment
Flow: PreAuthorization
Flow: Retain card
Flow: Silent abort
Banking Additional Flows
Banking Flow: BalanceInquiry
Banking Flow: Client Identification
Banking Flow: Card Identification
Banking Flow: Account Transfer
Banking Flow: Account Deposit
Banking Flow: Account Payout
Banking Flow: Parcel Acknowledgement
Banking Flow: Load PrePaid Phone
Guide Austrian Additional Flows
Austrian Flow: NGV Purchase without delay
The following flow describes an NGV purchase without any specific clearing delay set. The ngv_mode "AllowedWithFallback"
is used which indicates it the card used is not capable of NGV payments the terminal is allowed to make a fallback to a standard purchase. This flow shows a
successfully performed NGV payment which can be seen by checking the value ngv_used_flag, which is set to "true".
Austrian Flow: NGV Purchase with delay
In the flow below, additionally to the ngv_mode "AllowedWithFallback" also the
clearing_delay is set to define a specific clearing delay in days.
This means that the NGV payment clearing will be delayed by the amount of days specified. This flow shows a successful NGV payment including
a clearing delay.
Austrian Flow: NGV Purchase fallback with Non-NGV card
The following flow describes an NGV payment with ngv_mode "AllowedWithFallback" which
results in a fallback to a standard purchase due to the fact that the card used is not capable of NGV payments.
The ngv_used_flag is used to determine if the NGV payment was performed as such or if a fallback
was used. In this case the ngv_used_flag value is set to "false" which indicates that the requested
NGV payment was not successful and the fallback to a standard purchase has been done.
Austrian Flow: NGV Purchase mandatory with error
The following flow describes a mandatory NGV purchase transaction which could not be performed by the terminal.
As the used ngv_mode is "Mandatory" but the card used is not capable of NGV payments, the
transaction results in an error which means a result_code != '0' and an error payload as transaction response.
Logging
The TIM API is able to log an extensive set of events and actions within the TIM API. It's key that logs are created and stored properly. Logging enables support and makes bug-tracking much easier.
The TIM API C fires log events for every log_record. It's the application's responsibility to manage and store these.
In order to get notified about log-events, implement the callback function
ta_cb_publish_log_record
and register it with
ta_logger_set_global_logger
.
Note: The TIM SDK contains example code for how to manage and store log-records. You can find the files "timapi_loghelper.c" and "timapi_loghelper.h" under "C/Utils/" in the TIM SDK.
Log Level
The following logging levels exist:
- ta_c_ll_finest
- ta_c_ll_fine
- ta_c_ll_info
- ta_c_ll_warning
- ta_c_ll_severe
- ta_c_ll_off
Log Configuration
Note: ta_terminal_settings contains deprecated options regarding logging. Do not use these:
set_log_dirget_log_dirset_log_file_count_per_archiveget_log_file_count_per_archiveset_log_retain_archive_countget_log_retain_archive_countset_log_retain_file_countget_log_retain_file_count
C Language Specifics
Objects in TIM API C
The TIM API C is based on an object-type concept. Most TIM API functions will either take or return parameters
in shape of the "opaque type"
ta_object_t. For example:
ta_terminal_create will create a new terminal-instance, which returns a
ta_object_t. On the other hand terminal-function calls like
ta_terminal_get_terminal_id require the terminal-instance as parameter of type
ta_object_t.
Note: This concept introduces a behaviour similar to certain aspects of object-oriented programming to the environment of C. Similarities are as follows:
- For each object-type there are functions similar to getters and setters, in order to access the object-properties.
- The naming of getters and setters is as follows: ta_DATATYPE_get/set_PROPERTY
- e.g.:
ta_terminal_settings_get_terminal_id()
- For each object-type there are functions similar to methods, performing object-specific tasks.
- e.g.:
ta_terminal_login()
- e.g.:
- For certain object-types create-functions exist, which are similar to constructors.
- e.g.:
ta_string_create()
- e.g.:
Memory Management in TIM API C
The memory needed for each object will be allocated and freed by the TIM API itself. However, the user is responsible to release retained objects, when no longer needed. Retained objects are:
- Objects returned by the TIM API as retained objects (e.g.
terminal-instance created withta_terminal_create, or ahardware_information_response-instance returned byta_terminal_hardware_information). - Objects that the user explicitly retained by calling
ta_object_retain. Basically eachta_object_retainmust be paired with ata_object_release. The TIM API tells you if returned objects are already retained or not. An object that hasn't been retained, must not be released (would lead to errors)! Objects that are returned as not-retained are to read immediately or to explictely retain withta_object_retain.
(see header-documentation or this doxygen-dok to determine, if objects are retained / not retained. Most IDE support doxygen of header-documentation and will show these information while coding).
/* --- Create list -------------------------------------------------- */
ta_object_t myList = ta_object_invalid;
ta_list_create(&myList);
/* --- Add an integer ----------------------------------------------- */
// Create an object of type integer, since list can only contain
// ta_object_t-instances
ta_object_t myInteger = ta_object_invalid;
ta_integer_create(&myInteger, 1234);
ta_list_add(myList, myInteger);
// Important: User must release the integer-object. Either now or later.
ta_object_release(myInteger);
/* --- Get size of list --------------------------------------------- */
size_t myListSize;
ta_list_get_count(myList, &myListSize);
/* --- Receive first element of list -------------------------------- */
ta_object_t myListElement = ta_object_invalid;
ta_list_get_at(myList, 0, &myListElement);
// do something with element...
// - user is responsible to know how to read /
// process retreived objects from list
// - in our case here it`s an integer-object
int64_t myIntValue = 0;
ta_integer_get_value(myListElement, &myIntValue);
printf("MyIntValue: %Id\n", myIntValue);
// Important:
// - The list returns list elements as not retained!
// - List element must not be released!
/* --- Release list ------------------------------------------------- */
ta_object_release(myList);
// - At this point, myListElement is no longer (reliably) accessible.
// Since list has been released, all its elements have been released
// as well, if no one else is retaining the list elements.
// - If user still wants to use myListElement, he needs to call
// ta_object_retain(myListElement) right after receiving it from
// the list. In this case, he later needs to release the list
// element with ta_object_release(myListElement).Data Types in TIM API C
C doesn't provide data types / collections like string, boolean, list, timedate etc. Therefore the TIM API uses and provides a set of basic data types. In various places the TIM API requires or returns these data types.
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
boolean
|
A Boolean type (true/false) |
integer
|
An Integer type (64-bit) |
list
|
A list collection. Supports create, add, get, index of, remove and more. |
map
|
A map collection. Supports create, set, get, has, remove and more. |
object
|
The base object (see [Objects in TIM API`C`]). |
string
|
A String type. Null-terminated character sequence. |
timedate
|
Time-Date type. |